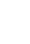Tree Root Protection Area
The advantages of tree root protection are multifaceted, impacting ecological health, urban sustainability, agricultural productivity, and infrastructure preservation. Here’s a structured overview of key benefits:
1. Ecological and Environmental Benefits
- Biodiversity Support
Protected roots maintain soil structure and microbial ecosystems, fostering mycorrhizal symbiosis (e.g., increased nutrient uptake via fungi like Rhizophagus irregularis), which enhances plant health and supports diverse soil organisms.
- Carbon Sequestration
Healthy roots promote tree longevity and vigor, enabling greater carbon storage in biomass and soil, critical for mitigating climate change.
- Soil Conservation
Roots stabilize soil, reducing erosion (e.g., in arid zones, drip irrigation and hydrogels protect roots while retaining moisture, preventing desertification).
2. Urban and Infrastructure Preservation
- Cost Reduction for Infrastructure
Root barriers (e.g., HDPE sheets) and permeable paving prevent root-induced damage to sidewalks, pipelines, and foundations, cutting repair costs by up to 70% in urban areas (e.g., Beijing case studies).
- Improved Urban Greenery Survival
Techniques like root zone mapping (GPR/BIM) and temporary fencing during construction reduce root disturbance, increasing transplant survival rates by 35% (e.g., Hangzhou gardens) and minimizing soil compaction.
- Aesthetic and Functional Urban Spaces
Root-friendly designs (e.g., permeable pavement, root plates) allow trees to thrive in compact urban environments, enhancing green infrastructure and air quality.
Introduction
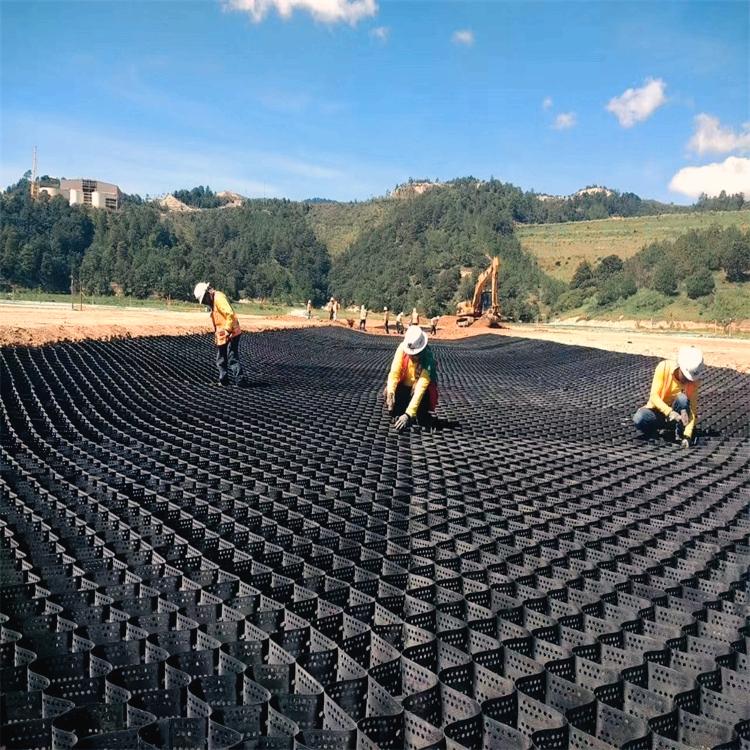
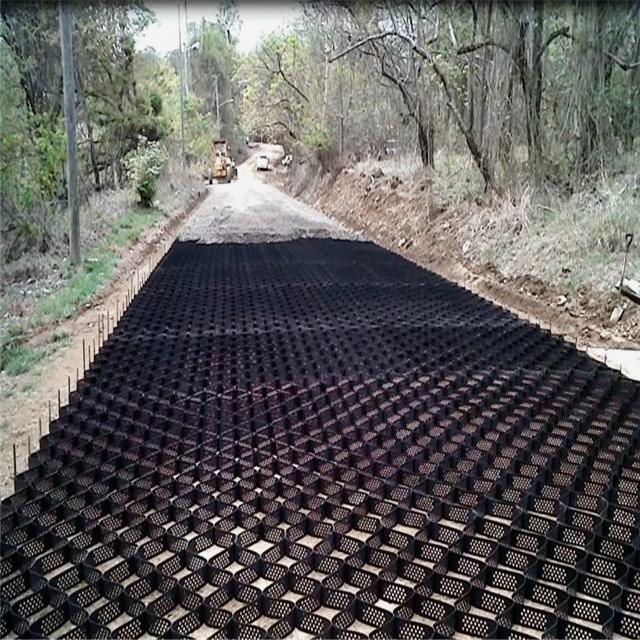
Tree root protection is designed to shield a tree’s root system. Within this area, safety of the root device and soil is a priority. The place is calculated to incorporate enough roots to make certain the viability of the tree.
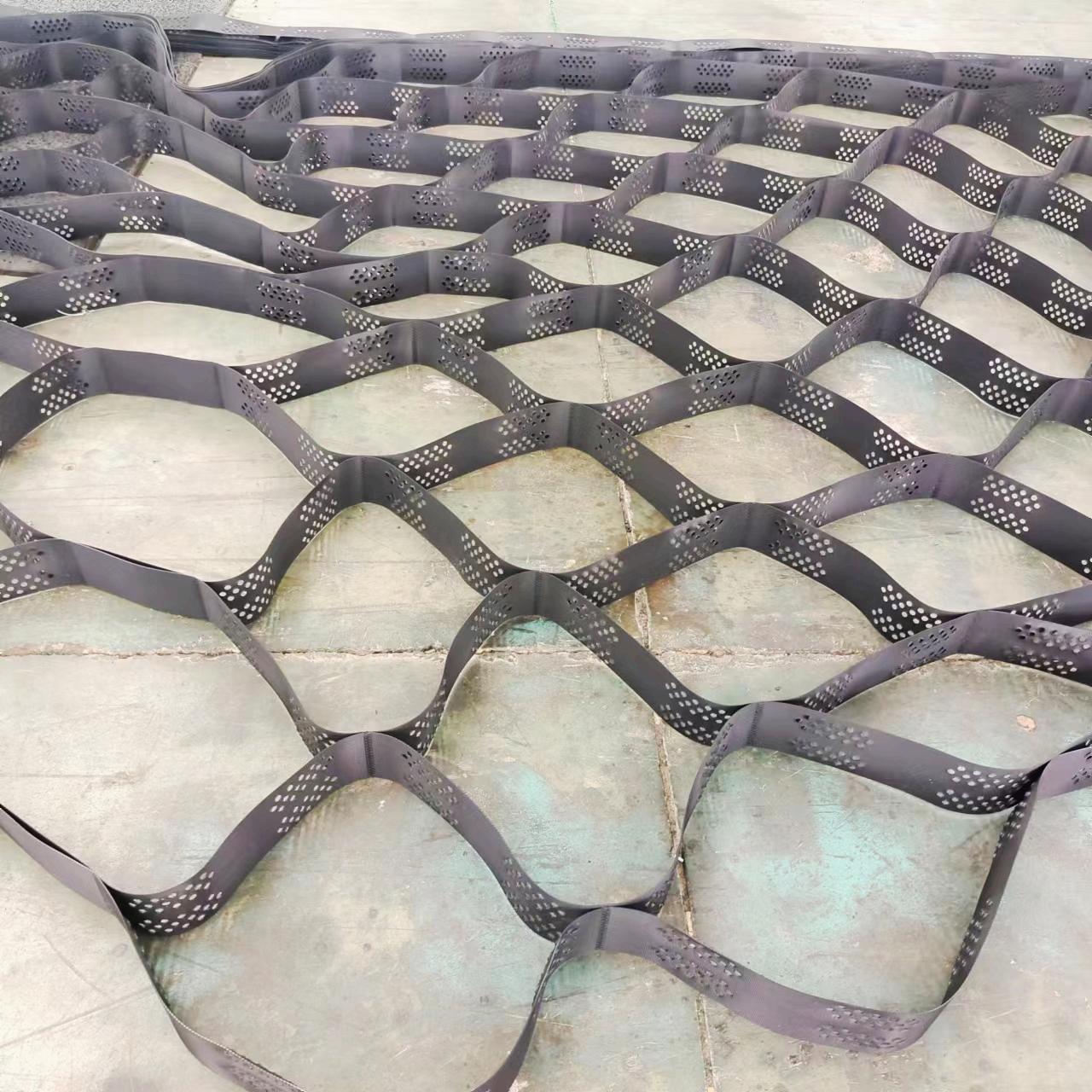
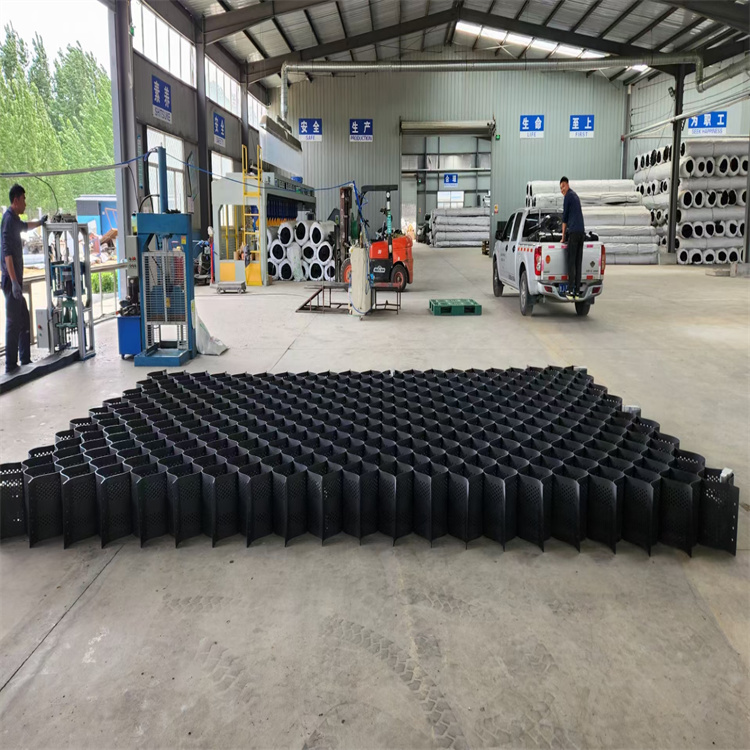
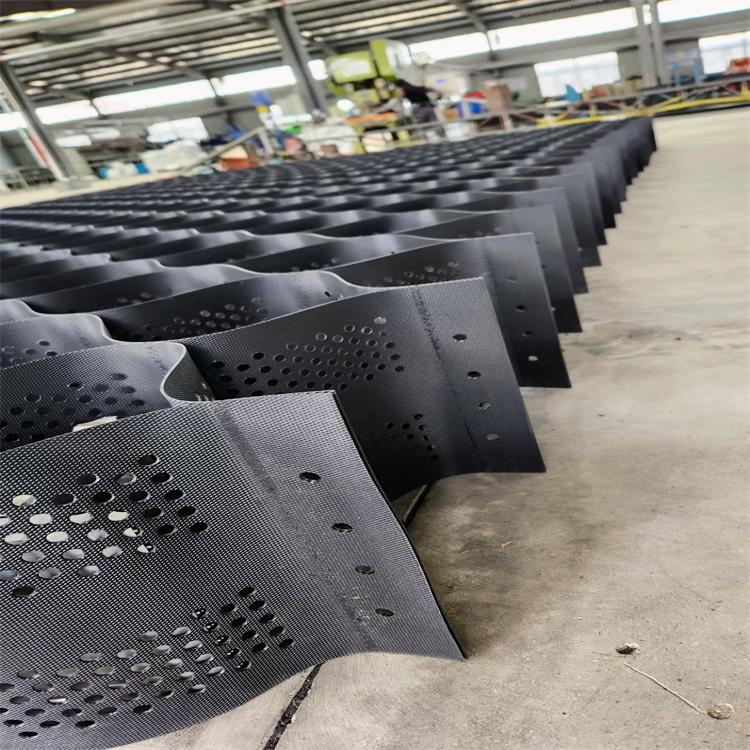
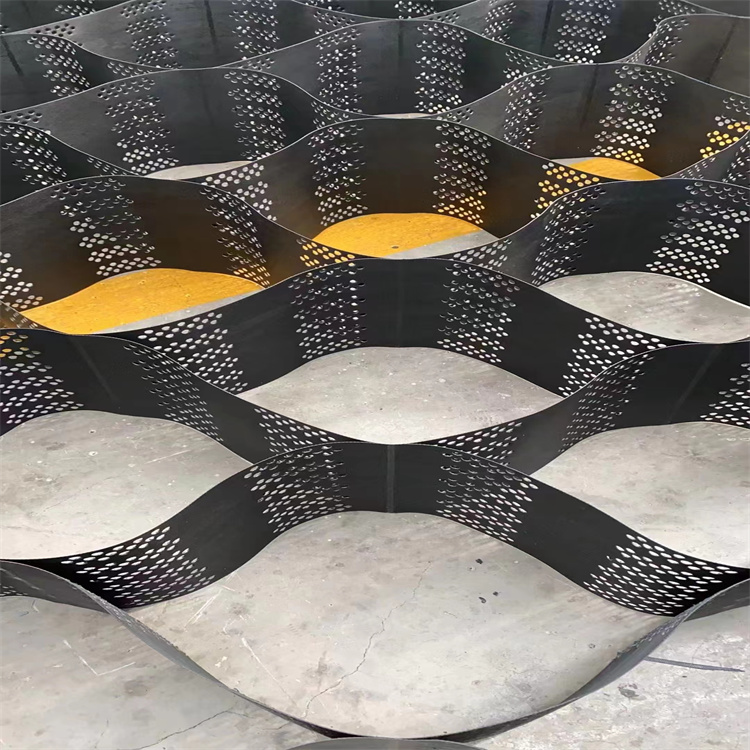
It has cellular structure and formed by the strong welding of polymer strips.It’s folded for transport and unfolded in application flexibly.Sand,gravel,soil or other material is filled in the geocell.It forms strong lateral constraints and large stiffness of the structure.Inspired by Mother Nature, these honeycombed shaped restraint systems contain perforations which allow water, or other fluids to pass through it; anchoring the in-fill into the soil, or subgrade firmly.
Features
Dynamic mechanical modulus (elastic stiffness): A greater modulus presents higher confinement and resistance to deformation below dynamic loading .
Creep resistance: Unless geocell rolls can hold their structure over a duration of time beneath sustained loads, they would be an luxurious fabric to work with. This is the place HDPE geocells acquire gain with incredible creep power properties.
Tensile strength: Higher tensile power permits the geocell to higher face up to deformation underneath repetitive, and special load kinds – a key component in deciding on the proper product.
Environmental durability: our merchandise are resistant to UV radiation, and additionally handled to deal with heat, and oxidation to keep away from degradation over a duration of time.
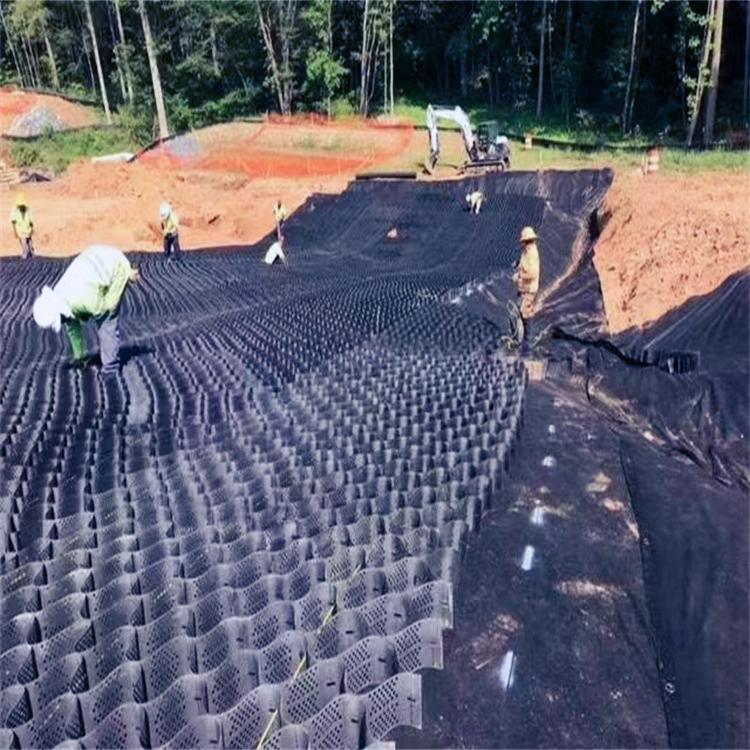
Application Installation
Removal of surface vegetation including turf can be removed using hand tools.
No topsoil should be excavated or removed.
The stabilising geogrid or geocomposite should be laid directly over the soil.
Edge boards may be used to contain the subbase and provide edge restraint. These will be pegged in place with wooden stakes.
The subbase material should be placed by hand or by lightweight tracked plant. The subbase should be cascaded forward onto the geogrid with the tracked plant operating only on top of the placed subbase. The initial layer thickness will be normally 150mm.
Tracking over by the lightweight plant will facilitate the aggregate interlock with the geogrid to establish the stabilised layer whilst minimising the compaction of the soil below.
A final roll with a small non-vibrating roller will firm the surface.
Parameters
Item | Property | Units | Value | |
Material | Polymer Density | g/cm3 | 0.94 | |
Carbon Black Content | % | 2.0 | ||
Oxidative Induction Time | Min | 20 | ||
Low Temperature Brittleness | ℃ | ≤-50 | ||
Vicat softening temperature | ℃ | ≥112 | ||
Environment Stress Crack Resistance F50 | hours | ≥800 | ||
Strip Properties | Sheet Thickness | mm | 1.1/1.2/1.5 | |
Sheet Tensile Strength | Mpa | ≥20 | ||
Sheet Surface | / | Smooth/Textured | ||
Color | / | Black/Yellow/Green | ||
Cell Depth | mm | 50/75/100/150/200/250 | ||
Seam Properties | Seam Peel Strength | N/10cm | ≥1000 |

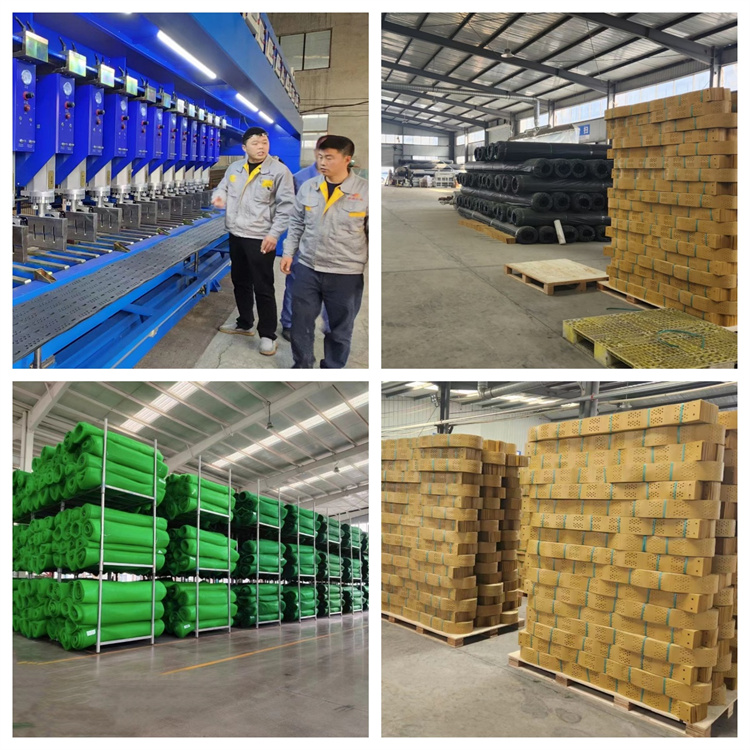
Our Factory
Customer Reviews