HDPE Uniaxial Geogrid: Engineered for Today’s Geo-technical Challenges
Introduction: The Advent of Geosynthetics in World Infrastructure
In the age of fast urbanization, climate protection and sustainable building, it is hot for the high performance geosynthetic materials. Of these, HDPE uniaxial geogrids specifically is an essential product in soil reinforcement and slope stability solutions around the globe. Constructed of high-density polyethylene, this unique geogrid provides superior tensile reinforcement capability in one direction, making it ideal for use over weak subgrades, steepened slopes and walls. With the surge in global infrastructure investments, it is important for B2B purchasers in civil engineering,construction and transportation to understand the technical benefits, market dynamics and applications of HDPE uniaxial geogrids.”
Market Overview
The global geosynthetics market, a key segment of which includes uniaxial geogrid products, is experiencing robust growth. Driven by massive investments in roadway networks, railway expansions, coastal protection, and mining operations, the market is projected to continue its upward trajectory. HDPE uniaxial geogrid is particularly favored in regions with challenging soil conditions or where cost-effective, durable solutions are mandated. Its primary function—to provide tensile reinforcement to granular soils—translates into longer-lasting infrastructure with reduced maintenance costs, a value proposition highly attractive to government agencies and private developers alike.
Several factors are propelling the demand for high-strength uniaxial geogrid:
· Infrastructure Renewal: Aging infrastructure in developed economies requires rehabilitation, often utilizing modern reinforcement techniques.
· Sustainable Construction: The use of geogrids reduces the need for virgin aggregate quarrying and extensive land excavation, promoting greener construction practices.
· Cost-Efficiency: Projects utilizing HDPE geogrid for soil reinforcement often see significant savings in both material and construction time compared to traditional methods.
· Regulatory Standards: Increasingly stringent engineering codes and standards for slope stability and embankment design mandate the use of certified reinforcement materials.
The trend is moving towards higher-performance polymers and manufacturing techniques that enhance long-term design strength (LTDS) and improve resistance to environmental stressors like UV radiation and chemical exposure.
Technical Deep Dive: Manufacturing and Properties of HDPE Uniaxial Geogrid
Understanding the manufacturing process is key to appreciating the performance of HDPE uniaxial geogrid. The production typically involves a multi-step process:
1. Extrusion: High-density polyethylene resin is extruded into a flat sheet.
2. Punching: The sheet is precisely punched to form a regular pattern of apertures.
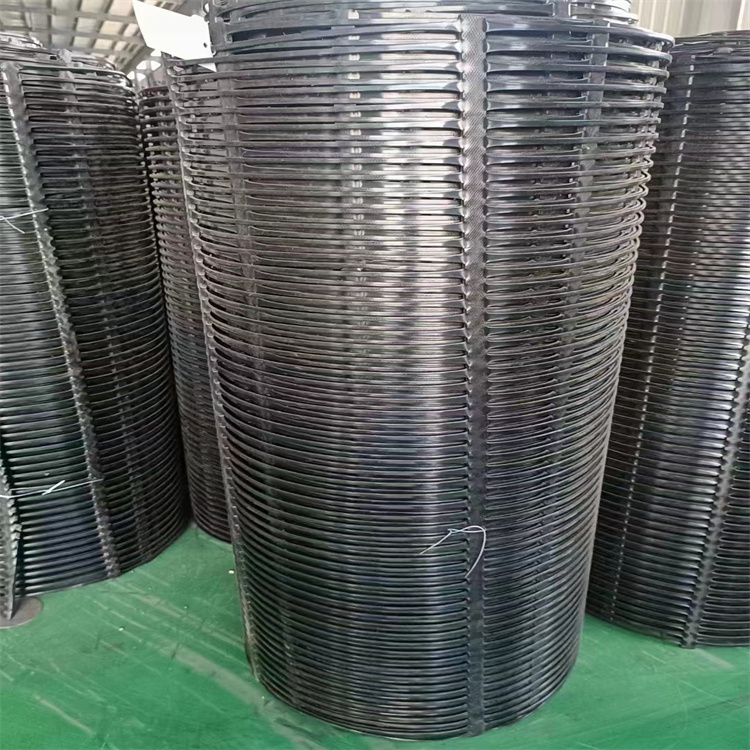
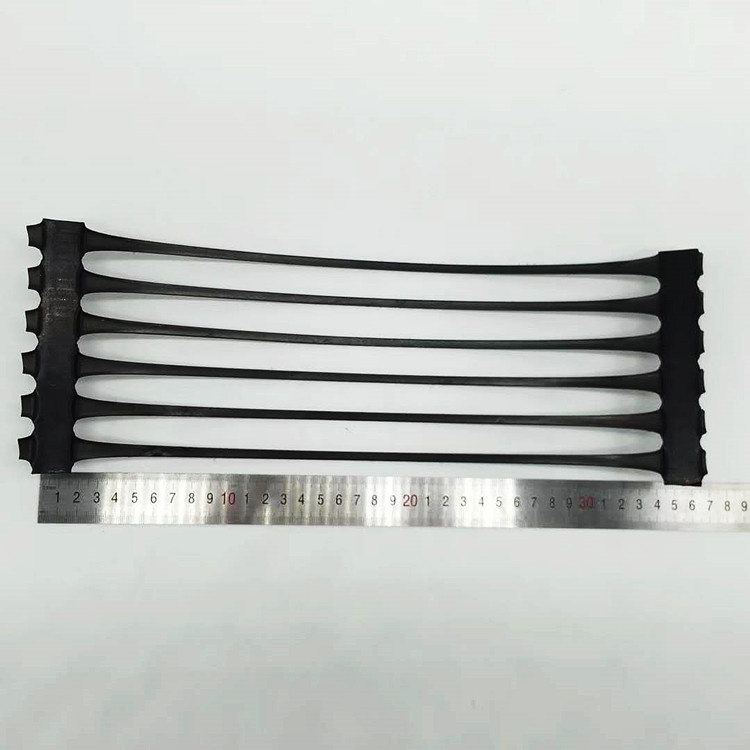
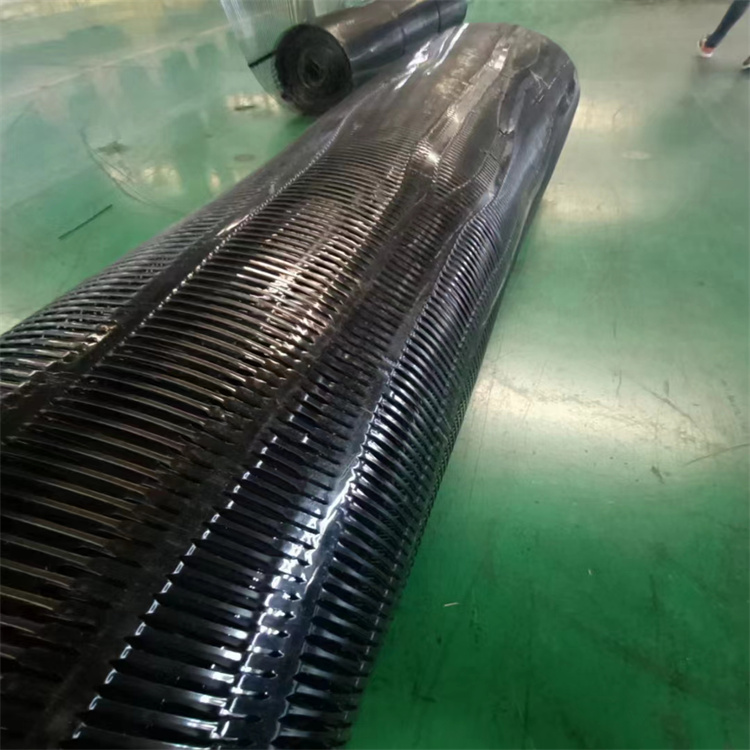
3. Stretching (Orientation): This is the most critical stage. The punched sheet is heated and stretched in a single, machine direction (uniaxial). This molecular orientation aligns the polymer chains, dramatically increasing the tensile strength and stiffness in that direction while creating the iconic rib-and-aperture structure.
4. Finishing: The stretched geogrid may be coated or further treated before being rolled for shipment.
Why Choose HDPE Material?
The choice of High-Density Polyethylene as the base polymer is deliberate. HDPE offers an exceptional balance of properties crucial for geotechnical applications:
· High Tensile Strength: Provides the necessary reinforcement to withstand soil stresses.
· Excellent Creep Resistance: Minimizes deformation under long-term constant load, a vital factor for permanent structures.
· Superior Chemical and Biological Resistance: Inert to most soils, leachates, and microorganisms, ensuring long-term performance without degradation.
· Durability: When formulated with carbon black for UV stabilization, UV stabilized HDPE geogrid can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight during and after installation.
Primary Applications and Installation Advantages
HDPE uniaxial geogrids are specifically engineered for applications where the primary tensile forces act in one direction. Their main uses include:
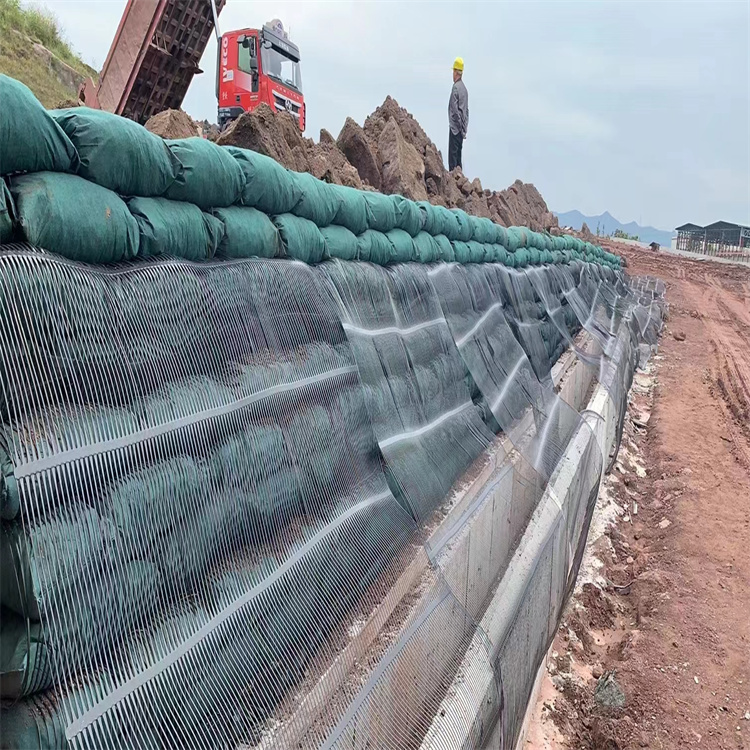
Reinforced Steep Slopes and Embankments
In roadway or railway cuttings and fills, geogrid for slope stabilization is placed between layers of compacted fill. The geogrid interacts with the soil particles through its apertures, creating a reinforced composite mass that allows for the construction of steeper, more stable slopes while using less land.
Retaining Walls
Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) walls are a premier application. Layers of uniaxial geogrid for retaining walls are embedded into the backfill soil, tying it to the wall facing. This creates a massive, coherent gravity structure that is often more economical and faster to build than conventional concrete walls.
Foundation Reinforcement
Beneath embankments built on very soft subsoils, a basal layer of HDPE uniaxial geogrid can distribute loads, reduce differential settlement, and improve overall stability.
Installation Brief: The installation process is straightforward, contributing to its popularity. The rolled geogrid material is laid out on a prepared subgrade, tensioned slightly to remove slack, and then backfilled with select granular material. Proper compaction over the geogrid is crucial to achieve optimal soil-grid interaction.
FAQ: Answers for B2B Buyers
Q1: What is the typical design life of an HDPE uniaxial geogrid, and what factors affect it?
A:A properly manufactured and installed HDPE uniaxial geogrid has a design life exceeding 100 years for many applications. Key factors include the polymer quality, carbon black content for UV resistance (for exposed periods), the chemical nature of the soil environment, and the actual long-term load it sustains. Always request certified test data for oxidative induction time (OIT) and creep resistance from your supplier.
Q2: How do I choose between a uniaxial and a biaxial geogrid?
A:The choice depends on the stress direction in your project. Use a uniaxial geogrid when the tensile forces are predominantly in one direction, such as in steep slopes, retaining walls, or embankment reinforcement. Choose a biaxial geogrid (strength in two perpendicular directions) for applications like road base stabilization where loads are spread in multiple directions. Consulting with a geotechnical engineer is recommended.
Q3: Can HDPE geogrids be used in exposed applications?
A:While HDPE geogrid has excellent durability, prolonged direct exposure to UV sunlight can degrade the polymer over time. For permanently exposed faces (like some wall applications), specify a UV stabilized HDPE geogrid with a high carbon black content. For temporarily exposed conditions during construction (typically up to 6 months), standard grades are usually sufficient, but follow the manufacturer's guidelines.
Q4: What certifications or test standards should I look for when sourcing?
A:Reputable manufacturers will provide test reports based on international standards such as ISO, ASTM, or GRI. Key tests include tensile strength (ASTM D6637), junction strength, aperture stability, and long-term creep tests. Certifications like CE marking or specific national approvals may be required for publicly funded projects.
Conclusion: Partner for Performance and Reliability
The selection of geosynthetic reinforcement is a critical engineering decision with long-term implications for project safety, durability, and cost. HDPE uniaxial geogrid, with its engineered strength, proven durability, and focused application benefits, represents a smart, sustainable choice for modern geotechnical challenges.
As you evaluate suppliers, look for partners who offer not just a product, but comprehensive technical support, certified quality data, and a deep understanding of international project requirements. Ensure your chosen HDPE uniaxial geogrid supplier can provide project-specific design guidance and reliable, on-time delivery to keep your projects on track.