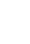HDPE Geomembrane 1mm
Unrivaled Chemical and Environmental Resistance
HDPE geomembrane liner demonstrates exceptional inertness to a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and industrial wastes, making it ideal for landfill liner and mining leach pad applications where leachate chemistry is harsh and unpredictable.
Superior Long-Term Durability
With a proven design life often exceeding 30 years when properly installed and protected, it offers a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution. Its resistance to punctures, tears, and stress cracking ensures long-term integrity.
Excellent Seam Integrity
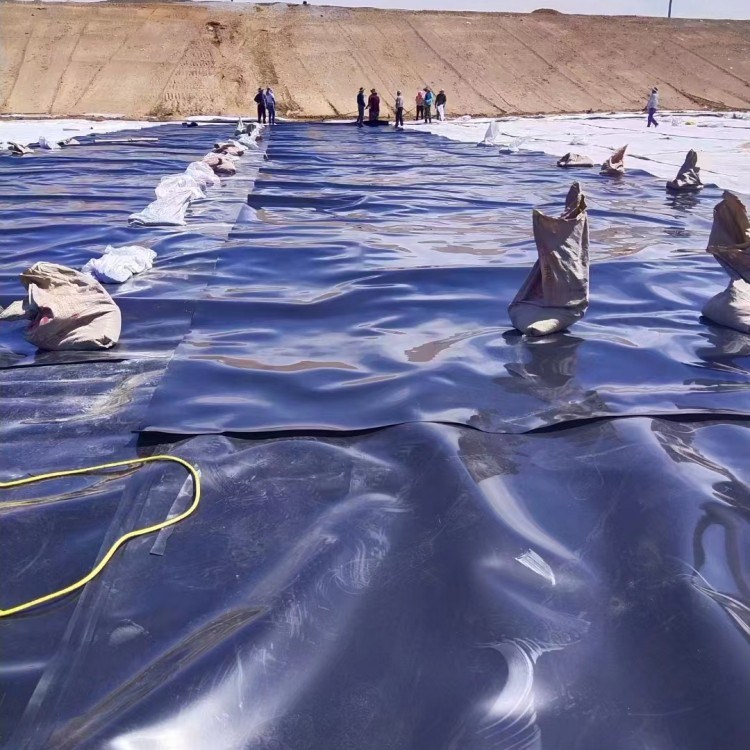
HDPE geomembrane sheets can be reliably and durably joined in the field using dual-track fusion welding equipment. This creates seams that are as strong, or stronger, than the parent material itself, ensuring a continuous, monolithic barrier—a critical factor for pond liner and reservoir liner applications.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Lifecycle
Despite a potentially higher initial material cost compared to some alternatives, its longevity, minimal maintenance requirements, and regulatory acceptance make it the most economical choice for permanent containment structures, reducing total cost of ownership.
Introduction: The Best of the Best in Fluid and Vapor Barrier Technology
In the world of geosynthetic engineering, where failure is not an option, HDPE geomembrane has always been the ultimate standard for impermeable lining systems. Made from high-density polyethylene resin—an advanced material known for its robustness and resistance to chemicals—HDPE geomembrane is processed into large, flexible sheets that serve as an almost totally impervious barrier to fluid migration and gas migration. With its excellent physical properties and proven longterm performance, it has become the material of choice for some of the world's most demanding environmental, hydraulic, and industrial containment projects.
There are very few points in any project as critical as determining the correct HDPE geomembrane liner plumbing. Whether it is the integrity of the project, compliance with regulations or long-term safety in operation depends on this decision. The following article sets out the technical specifications, advantages and specific uses of HDPE geomembranes—essential engineering components.
Product Characteristics: Engineered for Unrivaled Performance
The definition of HDPE geomembrane is a sum of its engineered properties. The top standard of containment performance in the most severe environment is collectively realized.
The makers of HDPE polymer argue that it is indispensable:
· High Crystalline Structure: Its molecular arrangement imparts excellent chemical resistance and low permeability, making it an effective barrier to a broad spectrum of leachates, hydrocarbons and gases.
· Great Toughness: When compounded properly with carbon black (to maintain UV stability), it enjoys exceptional resistance to UV radiation, oxidative degradation and extreme temperatures.
· High Tensile Strength and Elongation: Although stiffer than other kinds of flexible membrane such as LLDPE, modern HDPE geomembrane has an overall good stress-strain profile. It gives solid strength and toughness to withstand installation stresses and longterm subgrade settlements.
· Its low permeability coefficient is an important feature. The fact that HDPE geomembrane has a very high hydraulic conductivity means that water and steam cannot get though it at all, with its rate for preventing the passage of these materials below 8x10-11 m/s.2. Manufacturing Process and Main Specifications
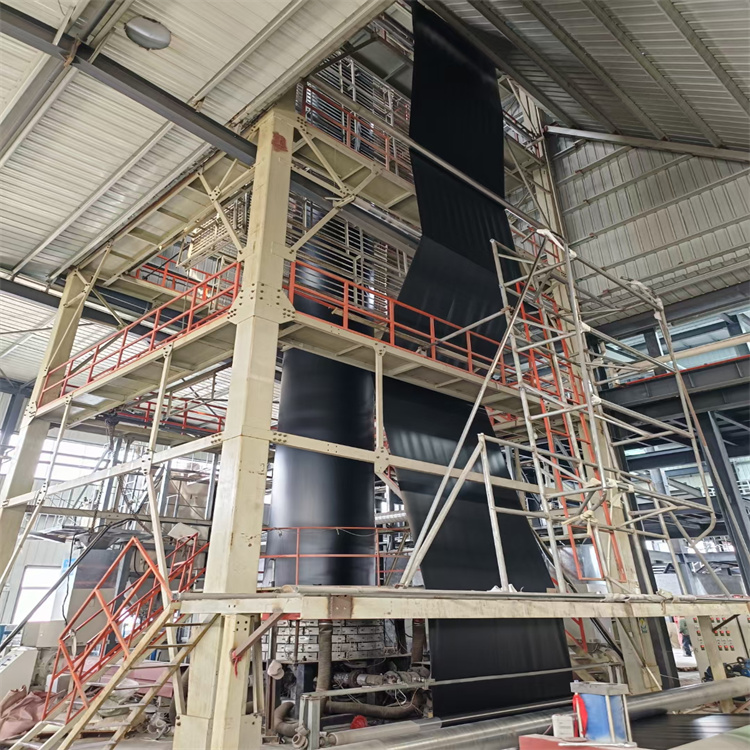
The production of high quality HDPE geomembrane is carried out by means of a flat-die extrusion process which ensures uniform consistency.
Resin Blending: The primary HDPE resin is blended with masterbatch (e.g., carbon black, antioxidants, UV stabilizers) to provide targeted properties.Extrusion Sheet Formation: After compounding, the sheet of molten material is squeezed out onto a flat die where it is then picked up by rollers in precision cooling units to harden into a solid piece of specified thickness.
Thickness and Widths: Standard thicknesses range between 0.75 mm (30 mils) to 3.0 mm (120 mils) and larger. The standard width is 7 m, but variations may be made when circumstances dictate something different from this size. 1.5 mm HDPE geomembrane (60 mils) is the common thickness for landfill linings.
A surface finish: HDPE geomembranes have either a smooth or textured finish. Textured HDPE geomembrane has surface projections, which greatly enhance angles of interface friction with soils as well as geosynthetics; it is therefore self-evident that much greater slope stability is obtained in these conditions.
Main advantages and functional benefits
The use of HDPE geomembrane has direct long-term benefits for the project owner and the environment.
Unique Chemical & Environmental Resistance
HDPE geomembrane liner has an unparalleled chemical resistance and environmental inertia, from general applications like anchorage and retaining walls to the more severe demands of landfills and mining leach pads where leachate chemistry is often highly unpredictable.
Long-Term Durability
Commonly expected design life is in excess of 30 years if properly installed and protected. This it is an inexpensive and economical long-term solution for the floors, hillsides, and pools. Its resistance to punctures, tearing, and stress cracking under load assures continuous operation free of trouble.
Superior Seam Integrity
The seams of HDPE geomembrane sheets can be created in the field, on a site with double track extrusion welder. These turns out clerks that are stronger than the original material, with continuity eliminating problems in ponds or reservoirs.
Cost-Effectiveness Across Lifecycle
Although it is more expensive than many other similar materials on a first cost basis, its longevity, low maintenance requirements and compliance with national standards ultimately make it an economic option for permanent containment structures—it will reduce total costs over the years.
Primary Application Areas
For key projects in a multiple high hazard industry, the specifications sheet leader is HDPE geomembrane.
Environmental Containment
· Landfills (Municipal & Hazardous): Leachate containment and groundwater protection, as primary and secondary landfill lining systems.
· Wastewater and Treatment Lagoons: It lines anaerobic ponds to ensure that the surrounding soil and water are not contaminated.
Water Management and Conservation
· Drinking Water Reservoirs: Holds drinking water safely. A potable water geomembrane often requires NSF 61 certification.
· Irrigation Canals and Ponds: Prevents water seepage from agricultural sites.
· Fire Protection and Decorative Ponds: A dependable waterproof pond liner with long service life.
Mining and Energy
· Heap Leach Pads and Tailings Dams: It contains process solutions in metal extraction. (mining geomembrane)
· Evaporation Ponds: For salt brine and process water management.
· Secondary Containment: For fuel storage tanks and industrial process areas.
Civil and Aquaculture
· Tunnel and Underground Waterproofing
· Fish and Shrimp Pond Liners
Construction Overview:
Professional installation is the key to its impressive performance.
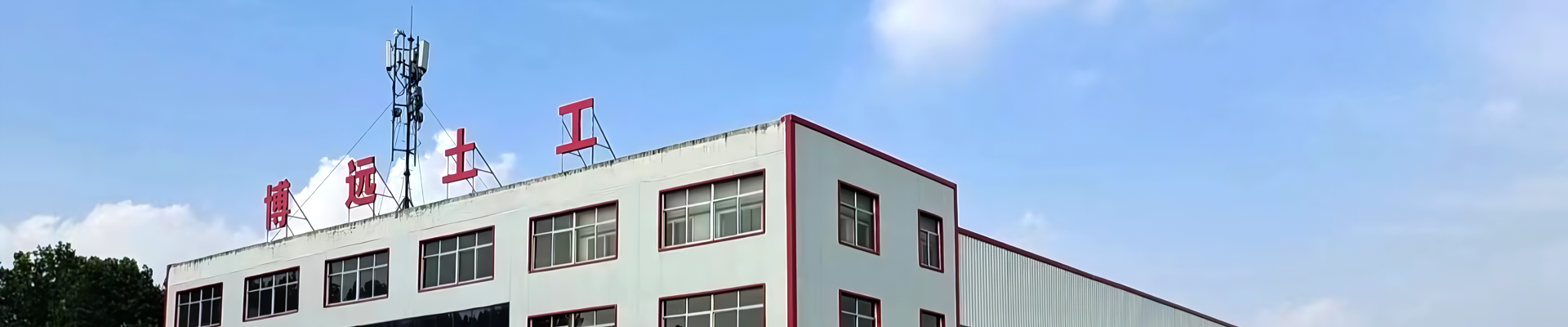
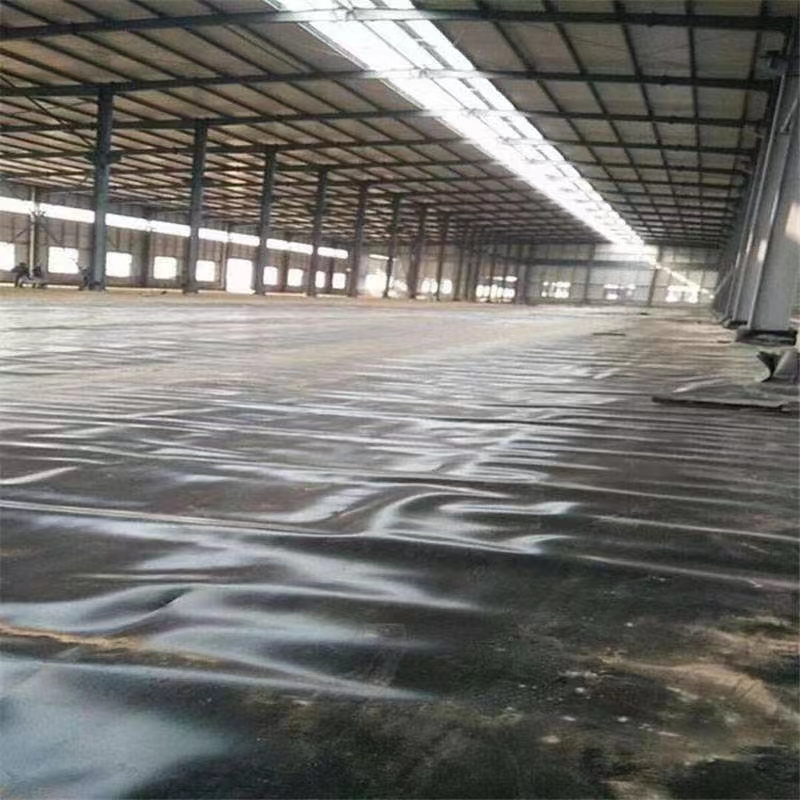
Subgrade Preparation: The subgrade should be made smooth, compact, and stable, without sharp objects. Panel Deployment: Geomembrane sheets should be unrolled and positioned with enough overlap for welding Seaming: Welding panels together using approved fusion wedge or extrusion technique tequniques, followed by non destructive (air pressure) and destructive (shear/peel) seam testing.
Protection: Immediate over-laid with specified protective layer(meaning non-woven geotextile or earth, or to assist UV protection and reduce harm from mechanical action).
FAQ For International Buyers And Specifiers
Q1: Differences Between Smooth And Textured HDPE Geomembrane; When Do I Need Textured?
A: The smooth HDPE geomembrane below bed applications is the standard product. Textured geomembranes on one side or both have a rough surface and that leads to high interfacial strength with surrounding soil or geosynthetics. This is necessary in steep slope lining (e.g., landfills and dams) to avoid sliding and improve stability of the slope. Any slope above a 3H:IV ratio must be lined with textured geomembrane.
Q2: Determining The Appropriate Thickness Of Geomembrane (e.g., 1.0mm Vs. 1.5mm Vs. 2.0mm) For My Project?
A: Thickness selection is based on: · Subgrade Conditions Worse subgrades require thicker geomembranes for enhanced puncture resistance. · Applied Stress High liquid heads (e.g., in deep reservoirs) and high overburden pressures (e.g., in landfills) demand greater thicknesses. · Design life and regulatory requirements Certain applications, such as primary landfill liners, have minimal regulatory thicknesses (often 1.5mm/60 mil). A geotechnical engineer should carry out design analyses to specify the correct thickness.
Q3: Can I use HDPE geomembrane in exposed situations, such as floating covers?
A: Yes, but it must be made in a specific way. Landfill geomembrane in particular must be made not only with enhanced UV resistance but also with antioxidant packages for use under cover. Moreover, most exposed geomembranes need to have a lighter color (such as white) in order to reflect heat and reduce thermal expansion, unlike the standard black lining used for buried applications.
Production Line
Our Lab
Customer Review